In today’s fast-paced digital world, internet speed is crucial. Whether you’re streaming your favorite show, working from home, or navigating through a new city, a reliable and fast internet connection is essential. This article dives into the intricacies of 4G, 5G, and WiFi technologies, exploring how they work, their benefits, and their limitations. We’ll also guide you through conducting speed tests and understanding the results, helping you choose the best connectivity option for your needs.
Understanding 4G Technology
4G, or Fourth Generation, is a mobile communication standard that significantly improved internet speeds and connectivity compared to its predecessor, 3G. It enables high-speed data transfer, supporting activities like HD video streaming, online gaming, and seamless browsing. 4G offers several advantages, including:High-Speed Internet: Capable of speeds up to 100 Mbps.Widespread Availability: Available in most urban and suburban areas.Improved Latency: Lower latency compared to 3G, enhancing real-time applications.
Limitations of 4G
Despite its benefits, 4G has limitations:Speed Variability: Speeds can fluctuate based on location and network congestion.Infrastructure Dependence: Performance is tied to the availability of 4G towers. 5G, or Fifth Generation, is the latest advancement in mobile network technology. It promises ultra-fast internet speeds, low latency, and the ability to connect more devices simultaneously, paving the way for innovations like smart cities and autonomous vehicles.
Benefits of 5G
5G brings several improvements: Blazing Fast Speeds: Potential to reach up to 10 Gbps.Ultra-Low Latency: Crucial for applications like remote surgery and virtual reality.Enhanced Capacity: Supports more connected devices per square kilometer.However, 5G also has its challenges:Limited Coverage: Still being rolled out, primarily available in major cities.Infrastructure Costs: High costs associated with deploying 5G infrastructure. WiFi is a technology that allows devices to connect to the internet wirelessly using radio waves. It’s commonly used in homes, offices, and public spaces to provide internet access.
Benefits of WiFi
WiFi offers several advantages:Convenience: Easy to set up and use.No Data Limits: Often unlimited data usage.Cost-Effective: Generally cheaper than mobile data plans.Limitations of WiFi WiFi has its downsides: Limited Range: Performance drops with distance from the router. Interference: Prone to interference from other electronic devices. Internet speed is typically measured using three key metrics: Download Speed: How quickly data is transferred from the internet to your device. Upload Speed: How quickly data is transferred from your device to the internet. Ping (Latency): The time it takes for data to travel from your device to the server and back.
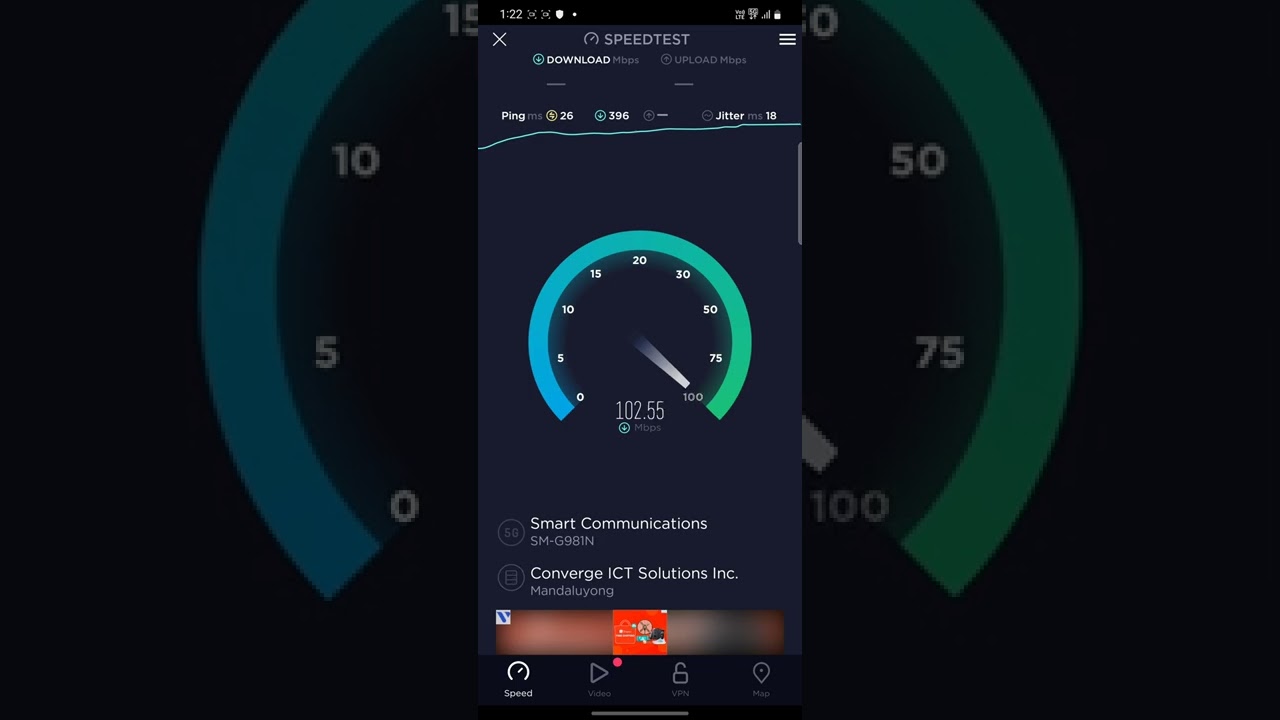
Tools for Measuring Internet Speed
Several tools can measure internet speed, including: Speedtest by Ookla: Popular and user-friendly. Fast.com by Netflix: Simple and focused on download speed. Google Fiber Speed Test: Reliable and straightforward. Conducting a speed test is simple: Choose a Tool: Select a reliable speed test tool. Connect to the Network: Ensure your device is connected to the network you want to test. Run the Test: Follow the on-screen instructions to start the test. Analyze Results: Review the download, upload, and ping results.
Best Practices for Accurate Results
To ensure accuracy: Close Background Applications: They can affect speed test results. Use a Wired Connection: For testing WiFi, use an Ethernet cable for the most accurate results. Test Multiple Times: Perform several tests at different times of the day. When comparing 4G and 5G speed tests, you’ll notice: Significantly Higher Speeds: 5G generally offers much faster download and upload speeds. Lower Latency: 5G’s latency is typically much lower than 4G’s.
Real-World Scenarios
In real-world use: 4G: Suitable for everyday activities like browsing and social media. 5G: Ideal for high-demand activities like streaming 4K videos and online gaming. Several factors can affect WiFi speed: Router Placement: Central location is best. Interference: Other electronics can interfere with the signal. Number of Devices: More devices can slow down the network.




5G
Ramesh
Hi
5G